Ready to dive into the world of blood types? Let's explore an intriguing aspect - the antigen in blood type A!
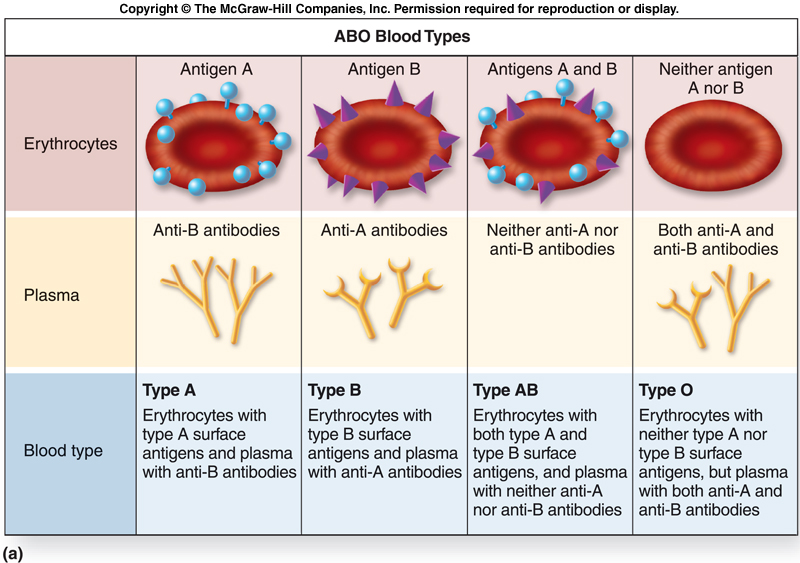
The antigen in blood type A is a specific protein found on the surface of red blood cells. It plays a crucial role in determining a person's blood type, which is a classification system that helps ensure safe blood transfusions and medical procedures.
The presence of the A antigen distinguishes blood type A from other blood types. Individuals with type A blood can only receive blood transfusions from type A or O donors, as their immune systems recognize the A antigen as foreign and attack red blood cells carrying other antigens, such as B.
Understanding blood type antigens is not just limited to transfusions. It has historical significance in the study of genetics and immunology, helping scientists unravel the complexities of human biology. Moreover, blood type A has been linked to certain health conditions and responses to diseases.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we'll uncover more fascinating aspects of the antigen in blood type A, its implications in medicine, and its significance in the broader field of biology.
Antigen in Blood Type A
The antigen in blood type A is a defining characteristic that shapes an individual's blood type and has significant implications in medicine and biology.
- Definition: Protein marker on red blood cells, distinguishing type A blood.
- Function: Determines blood type compatibility for safe transfusions.
- Genetics: Inherited from parents, following specific inheritance patterns.
- Immunology: Triggers immune responses when foreign blood types are introduced.
- Health Conditions: Linked to certain health conditions, such as susceptibility to infections.
- Historical Significance: Played a role in the development of blood typing and transfusion practices.
- Medical Applications: Used in blood typing tests, organ transplants, and forensic science.
These aspects collectively highlight the multifaceted nature of the antigen in blood type A, underscoring its importance in various fields. Understanding these aspects provides a deeper appreciation of blood type systems, immune responses, and the intricate workings of human biology.
Definition
The definition provided encapsulates the fundamental nature of the antigen in blood type A. This protein marker, present on the surface of red blood cells, acts as a unique identifier, distinguishing type A blood from other blood types. Its presence determines an individual's blood type, which is a crucial factor in ensuring compatible blood transfusions and preventing adverse immune reactions.
The protein marker's role in distinguishing blood types stems from its ability to trigger specific immune responses. When red blood cells carrying foreign antigens, such as type B, are introduced into an individual with type A blood, the immune system recognizes the foreign antigens as invaders and mounts an attack. This incompatibility highlights the importance of matching blood types during transfusions to avoid life-threatening complications.
Understanding the connection between the protein marker and blood type A has significant practical implications. It enables medical professionals to determine an individual's blood type accurately, ensuring safe and effective blood transfusions. Moreover, it has applications in organ transplants, where tissue compatibility is paramount to prevent rejection. Furthermore, in forensic science, blood type analysis plays a vital role in identifying individuals and solving crimes.
Function
The antigen in blood type A plays a crucial role in determining blood type compatibility, which is essential for safe and effective blood transfusions. When blood is transfused from one individual to another, the recipient's immune system checks for the presence of foreign antigens on the donor's red blood cells. If foreign antigens are detected, the immune system attacks the transfused red blood cells, leading to a potentially life-threatening condition called a transfusion reaction.
The antigen in blood type A is specifically responsible for determining compatibility with type A blood. Individuals with type A blood have the A antigen on their red blood cells, and their immune system will recognize and attack red blood cells carrying other antigens, such as type B. Therefore, individuals with type A blood can only receive blood transfusions from donors with type A or type O blood (which lacks both A and B antigens).
Understanding the function of the antigen in blood type A is crucial for ensuring safe blood transfusions. By matching blood types based on the presence or absence of specific antigens, medical professionals can prevent transfusion reactions and their associated complications. This understanding has revolutionized transfusion practices and greatly improved patient outcomes.
Genetics
The connection between genetics and the antigen in blood type A lies in the inheritance patterns that determine an individual's blood type. Blood type is a genetically determined characteristic, passed down from parents to children according to specific rules of inheritance.
- Alleles and Inheritance: Blood type is controlled by three alleles: A, B, and O. Each individual inherits two alleles, one from each parent. The A and B alleles are dominant, while the O allele is recessive.
- Phenotype Expression: The combination of alleles inherited determines an individual's blood type phenotype. Individuals with two A alleles have type A blood, those with two B alleles have type B blood, those with one A and one B allele have type AB blood, and those with two O alleles have type O blood.
- Predicting Blood Type Inheritance: Understanding inheritance patterns allows medical professionals to predict the possible blood types of offspring based on the blood types of their parents. This knowledge is crucial in situations such as blood transfusions and organ transplants, where blood type compatibility is essential.
The genetic basis of blood type A has significant implications in medicine and biology. It provides a framework for understanding blood type inheritance and compatibility, ensuring safe and effective blood transfusions and organ transplants. Moreover, it contributes to the broader field of genetics by elucidating the patterns of inheritance for specific traits.
Immunology
The antigen in blood type A plays a pivotal role in triggering immune responses when foreign blood types are introduced. This immunological aspect is central to understanding the significance of the antigen in blood type A.
When red blood cells carrying foreign antigens, such as type B antigens, enter the bloodstream of an individual with type A blood, the immune system recognizes these foreign antigens as invaders. This recognition triggers an immune response, leading to the production of antibodies that target and destroy the foreign red blood cells.
The immune response triggered by the antigen in blood type A is crucial for protecting the body from foreign invaders. However, in the context of blood transfusions, this immune response can pose challenges. If an individual receives a blood transfusion from a donor with an incompatible blood type, the recipient's immune system will attack the transfused red blood cells, leading to a transfusion reaction.
Understanding the immunological connection between the antigen in blood type A and immune responses is essential for ensuring safe and effective blood transfusions. By matching blood types based on the presence or absence of specific antigens, medical professionals can prevent transfusion reactions and their associated complications.
Health Conditions
The antigen in blood type A has been linked to certain health conditions, including an increased susceptibility to certain infections. This connection highlights the broader implications of blood type beyond blood transfusions and compatibility.
- Increased Susceptibility to Infections: Studies have shown that individuals with blood type A may be more susceptible to certain infections, such as norovirus and rotavirus. The A antigen on red blood cells may serve as an attachment point for these viruses, facilitating their entry into the body.
- Immune System Response: The immune system's response to the antigen in blood type A may contribute to the increased susceptibility to infections. Individuals with type A blood may have an altered immune response that makes them more vulnerable to certain pathogens.
- Variations in Immune Genes: Researchers have identified variations in immune genes that may be associated with blood type A and an increased susceptibility to infections. These genetic variations could influence the function of immune cells and their ability to fight off certain infections.
Understanding the connection between the antigen in blood type A and health conditions can help researchers and medical professionals better understand the complex relationship between blood type and overall health. Further research is needed to explore these associations and determine the mechanisms underlying the increased susceptibility to infections in individuals with blood type A.
Historical Significance
The historical significance of the antigen in blood type A lies in its pivotal role in the development of blood typing and transfusion practices, revolutionizing the field of medicine.
Karl Landsteiner's groundbreaking discovery of the ABO blood group system in 1901 marked a turning point in understanding blood compatibility. Landsteiner identified the presence of specific antigens, including the A antigen, on the surface of red blood cells. This discovery laid the foundation for blood typing, enabling the classification of blood into different types based on the presence or absence of these antigens.
The identification of the antigen in blood type A allowed researchers to understand why some blood transfusions were successful, while others resulted in life-threatening reactions. By matching blood types based on antigen compatibility, medical professionals could prevent transfusion reactions and ensure the safe administration of blood transfusions.
The development of blood typing and transfusion practices based on the antigen in blood type A has had a profound impact on healthcare. Blood transfusions have become a life-saving procedure, enabling the treatment of various conditions, including blood loss, anemia, and certain diseases.
Today, blood typing remains an essential component of modern medicine, ensuring safe and effective blood transfusions worldwide. The historical significance of the antigen in blood type A underscores its fundamental importance in shaping transfusion practices and improving patient outcomes.
Medical Applications
The antigen in blood type A finds extensive applications in the medical field, particularly in blood typing tests, organ transplants, and forensic science. Understanding its role in these applications deepens our comprehension of its significance.
In blood typing tests, the antigen in blood type A is crucial for determining an individual's blood type. By testing for the presence or absence of the A antigen, medical professionals can classify blood into different types, such as A, B, AB, and O. This information guides safe blood transfusions, preventing potentially life-threatening reactions. Blood typing also plays a vital role in organ transplants, ensuring compatibility between the donor and recipient organs.
In forensic science, the antigen in blood type A aids in identifying individuals and solving crimes. Blood type analysis, along with other forensic techniques, helps establish connections between suspects and crime scenes. By comparing blood samples found at crime scenes to blood samples from potential suspects, forensic experts can narrow down the pool of suspects and strengthen their cases.
The medical applications of the antigen in blood type A underscore its practical significance in healthcare and beyond. Its role in ensuring safe blood transfusions, successful organ transplants, and reliable forensic investigations highlights its indispensable value in modern medicine and law enforcement.
FAQs on Antigen in Blood Type A
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions about the antigen in blood type A, offering a concise and informative overview of the topic.
Question 1: What is the role of the antigen in blood type A?The antigen in blood type A is a protein marker found on the surface of red blood cells. It plays a crucial role in determining blood type compatibility for safe blood transfusions and organ transplants.
Question 2: How does the antigen in blood type A affect blood compatibility?Individuals with type A blood have the A antigen on their red blood cells. They can only receive blood transfusions from donors with type A or type O blood, as their immune systems recognize other antigens as foreign and attack them.
Question 3: How is the antigen in blood type A inherited?Blood type, including the presence of the A antigen, is genetically determined and inherited from parents according to specific inheritance patterns involving alleles.
Question 4: Can the antigen in blood type A affect susceptibility to infections?Studies have suggested a potential link between blood type A and increased susceptibility to certain infections, such as norovirus and rotavirus. However, further research is needed to fully understand this connection.
Question 5: What is the historical significance of the antigen in blood type A?The discovery of the antigen in blood type A by Karl Landsteiner in 1901 revolutionized blood typing and transfusion practices, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of blood transfusions.
Question 6: What are the medical applications of the antigen in blood type A?The antigen in blood type A is used in blood typing tests, organ transplants, and forensic science, playing a vital role in healthcare and investigations.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive understanding of the antigen in blood type A, addressing common questions and misconceptions. By delving into these aspects, we gain a deeper appreciation of its significance in medicine, genetics, and various other fields.
To further explore the topic, the next section will delve into the implications of the antigen in blood type A for blood transfusions and organ transplants, highlighting its practical applications in healthcare.
Conclusion
In this exploration of the antigen in blood type A, we have delved into its fundamental role in determining blood type compatibility, its genetic inheritance, immunological significance, and practical applications in medicine and beyond. This antigen serves as a defining characteristic of red blood cells, influencing an individual's blood type and susceptibility to certain health conditions.
Understanding the antigen in blood type A is crucial for ensuring safe blood transfusions and successful organ transplants. Its discovery revolutionized transfusion practices, preventing life-threatening reactions and improving patient outcomes. Moreover, blood typing based on the A antigen plays a vital role in forensic investigations, aiding in the identification of individuals and the resolution of crimes.
As we continue to unravel the complexities of human biology, the antigen in blood type A remains an intriguing subject of research. Further exploration of its associations with health conditions and its potential implications for personalized medicine hold promise for advancing healthcare and improving human well-being.
How Many Legs Does A Narrative Text Have?
Does Hot Chocolate Always Contain Dairy? Find Out Here
How To Effortlessly Move An Object To The Origin In AutoCAD | Beginner's Guide

Blood Antigen Chart

COVID19 Exploring the impact for people with different ABO blood
Standing on The Avalon What does a lab tech do? Part deux