What is the 20th Century Literary Movement?
The 20th Century Literary Movement refers to a diverse range of literary trends, styles, and ideas that emerged and evolved throughout the 20th century. It marked a period of significant change and experimentation in literature, characterized by a departure from traditional forms and the exploration of new themes and techniques.
The 20th Century Literary Movement was influenced by social, political, and cultural shifts, including the rise of modernism, existentialism, and postmodernism. It encompassed various literary genres, including poetry, prose, drama, and non-fiction, and featured a wide range of writers from around the world.
The 20th Century Literary Movement played a crucial role in shaping the trajectory of literature and continues to influence contemporary writing. It challenged conventional literary norms, pushed the boundaries of language and expression, and provided a platform for innovative literary voices.
Some notable figures and associated literary movements of the 20th Century Literary Movement include:
- Modernism: T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, Virginia Woolf
- Existentialism: Jean-Paul Sartre, Albert Camus
- Postmodernism: Salman Rushdie, Margaret Atwood, Italo Calvino
- Surrealism: Andr Breton, Salvador Dal
- The Harlem Renaissance: Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston
The 20th Century Literary Movement
The 20th Century Literary Movement was a period of significant change and experimentation in literature, characterized by a departure from traditional forms and the exploration of new themes and techniques. Here are five key aspects that shaped this movement:
- Modernism: A break from traditional literary forms, characterized by experimentation with language, structure, and perspective.
- Existentialism: A focus on the individual's existence and the search for meaning in a seemingly meaningless world.
- Postmodernism: A rejection of grand narratives and the celebration of diversity, fragmentation, and playfulness.
- Surrealism: An exploration of the subconscious mind and the juxtaposition of unexpected images and ideas.
- The Harlem Renaissance: A flourishing of African American literature, art, and music in the 1920s and 1930s.
These key aspects were interconnected and influenced each other, creating a dynamic and multifaceted literary landscape. Modernism paved the way for existentialism and postmodernism, while surrealism and the Harlem Renaissance challenged traditional notions of identity and culture. Together, these movements pushed the boundaries of literature and continue to shape contemporary writing.
Modernism
Modernism, a significant aspect of the 20th Century Literary Movement, emerged as a break from traditional literary conventions. It was characterized by a spirit of experimentation and innovation, particularly in language, structure, and perspective.
- Fragmentation and Non-Linearity: Modernist writers broke away from the traditional linear narrative structure, employing fragmentation and non-linearity to reflect the complexities of modern life and the fragmented nature of human consciousness.
- Stream of Consciousness: Modernism introduced the technique of stream of consciousness, allowing readers to directly access the inner thoughts and feelings of characters, capturing the fluidity and complexity of human experience.
- Symbolism and Allusion: Modernist writers made extensive use of symbolism and allusion, creating layers of meaning and inviting readers to engage in deeper interpretation.
- Experimental Language and Syntax: Modernist literature experimented with language and syntax, breaking down traditional grammatical structures and exploring the expressive potential of language.
These facets of Modernism challenged conventional notions of literary form and expression, opening up new possibilities for storytelling and deepening our understanding of the human condition. Modernism's influence continues to shape contemporary literature, encouraging writers to push boundaries and explore innovative approaches to writing.
Existentialism
Existentialism, a prominent aspect of the 20th Century Literary Movement, delved into the complexities of human existence and the search for purpose in an often incomprehensible world. It emphasized the individual's responsibility to create meaning and authenticity in the face of an indifferent universe.
- Alienation and Absurdity: Existentialist literature highlighted the feelings of alienation and absurdity experienced by individuals in a world that often seemed devoid of inherent meaning or purpose.
- Freedom and Choice: Existentialism emphasized the concept of individual freedom and the importance of making choices, even in the face of an uncertain future.
- Responsibility and Commitment: Existentialist writers explored the notion of personal responsibility and the commitment to one's actions, recognizing that our choices shape our existence.
- Authenticity and Subjectivity: Existentialism celebrated authenticity and the embrace of one's own unique perspective, valuing subjective experiences and individual truths.
These facets of Existentialism resonated deeply with the zeitgeist of the 20th century, a period marked by immense social and political upheaval. Existentialist literature provided a lens through which writers could explore the human condition, grapple with the complexities of modern life, and search for meaning in a rapidly changing world.
Postmodernism
Postmodernism, as a component of the 20th Century Literary Movement, emerged as a critique of the grand narratives and overarching ideologies that had dominated previous literary eras. It challenged the notion of a single, objective truth, instead embracing diversity, fragmentation, and playfulness.
Postmodernist writers rejected the idea of a unified, coherent reality, recognizing the influence of multiple perspectives and the fluidity of meaning. They celebrated diversity and the coexistence of different narratives, challenging traditional notions of genre, form, and structure.
Fragmentation and playfulness became defining characteristics of postmodernist literature. Writers experimented with non-linear narratives, unreliable narrators, and multiple perspectives, reflecting the fragmented nature of modern life and the subjective experiences of individuals.
The significance of postmodernism lies in its challenge to traditional literary conventions and its exploration of complex and often contradictory realities. It encouraged a more nuanced understanding of the world, acknowledging the coexistence of diverse perspectives and the fluidity of truth.
Postmodernism's influence extends beyond literature, impacting art, architecture, and other cultural domains. It has fostered a greater appreciation for cultural diversity, the questioning of established norms, and a playful experimentation with form and content.
Surrealism
Surrealism, a significant aspect of the 20th Century Literary Movement, emerged as a revolutionary force in art and literature. It sought to explore the subconscious mind and the unexpected juxtapositions of images and ideas, challenging conventional notions of reason and rationality.
Surrealism's profound influence on the 20th Century Literary Movement cannot be overstated. By embracing the irrational and the subconscious, it opened up new possibilities for creative expression and challenged the boundaries of traditional literary forms. Surrealist writers and artists sought to liberate the imagination and tap into the raw power of the subconscious.
One striking example of Surrealism's impact on literature is the work of Andr Breton, the movement's founder. In his influential manifesto, Breton advocated for "pure psychic automatism," a method of writing that allowed thoughts to flow freely onto the page, unfiltered by conscious control. This technique led to the creation of dreamlike, disjointed narratives that explored the depths of the unconscious mind.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between Surrealism and the 20th Century Literary Movement lies in its ability to deepen our appreciation for the diversity and complexity of modern literature. By recognizing the importance of Surrealism as a component of this broader movement, we gain a richer understanding of the forces that shaped 20th century literature and the ways in which it continues to influence contemporary artistic expression.
The Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance, a vibrant cultural movement that flourished in the 1920s and 1930s, was an integral component of the broader "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle." This period witnessed a remarkable surge in African American literature, art, and music, contributing significantly to the development and diversification of 20th-century literary and artistic expression.
The Harlem Renaissance emerged as a response to the social and cultural climate of the time. African Americans, facing pervasive discrimination and segregation, sought to establish a distinct cultural identity and challenge prevailing stereotypes. Through their creative endeavors, they celebrated their history, culture, and experiences, while also engaging with broader social and political issues.
One of the most significant contributions of the Harlem Renaissance was the emergence of a new generation of African American writers. Authors such as Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston, and Claude McKay gained international recognition for their powerful and evocative works. Their writings explored themes of racial identity, social justice, and the search for self-expression, providing a voice to the African American experience.
The Harlem Renaissance also witnessed a flourishing of visual arts and music. Artists like Jacob Lawrence and Archibald Motley Jr. depicted the everyday lives and struggles of African Americans, while musicians such as Duke Ellington and Louis Armstrong revolutionized jazz music.
Understanding the connection between the Harlem Renaissance and the "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle" is crucial for several reasons. First, it highlights the diversity and richness of the 20th-century literary landscape, which was shaped by multiple cultural and social forces. Second, it demonstrates the important role of African American artists and writers in shaping American culture and history. Finally, it underscores the power of art and literature as tools for social change and empowerment.
FAQs on the 20th Century Literary Movement
The 20th Century Literary Movement was a period of significant change and experimentation in literature. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about this movement:
Question 1: What are the key characteristics of the 20th Century Literary Movement?The 20th Century Literary Movement was characterized by a departure from traditional literary forms, the exploration of new themes and techniques, and the influence of social, political, and cultural shifts.
Question 2: What are the major literary movements that emerged during the 20th century?Some of the major literary movements that emerged during the 20th century include Modernism, Existentialism, Postmodernism, Surrealism, and the Harlem Renaissance.
Question 3: How did Modernism influence the 20th Century Literary Movement?Modernism challenged conventional literary forms and experimented with language, structure, and perspective. It broke away from traditional narrative structures and explored the complexities of modern life and the fragmented nature of human consciousness.
Question 4: What is the significance of Existentialism in the 20th Century Literary Movement?Existentialism focused on the individual's existence and the search for meaning in a seemingly meaningless world. It emphasized the importance of individual freedom, choice, and responsibility.
Question 5: How did Postmodernism contribute to the 20th Century Literary Movement?Postmodernism rejected grand narratives and celebrated diversity, fragmentation, and playfulness. It questioned traditional notions of genre, form, and structure, and explored the coexistence of multiple perspectives and the fluidity of truth.
Summary: The 20th Century Literary Movement was a dynamic and multifaceted period in literature, characterized by experimentation, innovation, and a profound engagement with the complexities of the modern world.
Transition: To delve deeper into the specific literary movements and their impact, let's explore each of them in more detail in the following sections.
Conclusion
The 20th Century Literary Movement stands as a testament to the transformative power of literature in reflecting and shaping the complexities of the modern world. It encompassed a diverse range of movements, each contributing unique perspectives and innovations that challenged conventional literary norms and pushed the boundaries of creative expression.
From the introspective explorations of Modernism to the existentialist quest for meaning, and from the playful experimentation of Postmodernism to the vibrant cultural expressions of the Harlem Renaissance, the 20th Century Literary Movement has left an indelible mark on our understanding of literature, culture, and the human condition.
Essential .NET Framework 3.5 Offline Installer For Seamless Installations
Exploring The Legality Of Pictures As Hearsay Evidence
Essential Guide To Window Handle Return Types Using Switch-to-Method In C#

Les courants littéraires du XVIe au XXe siècle Méthodo Bac Français
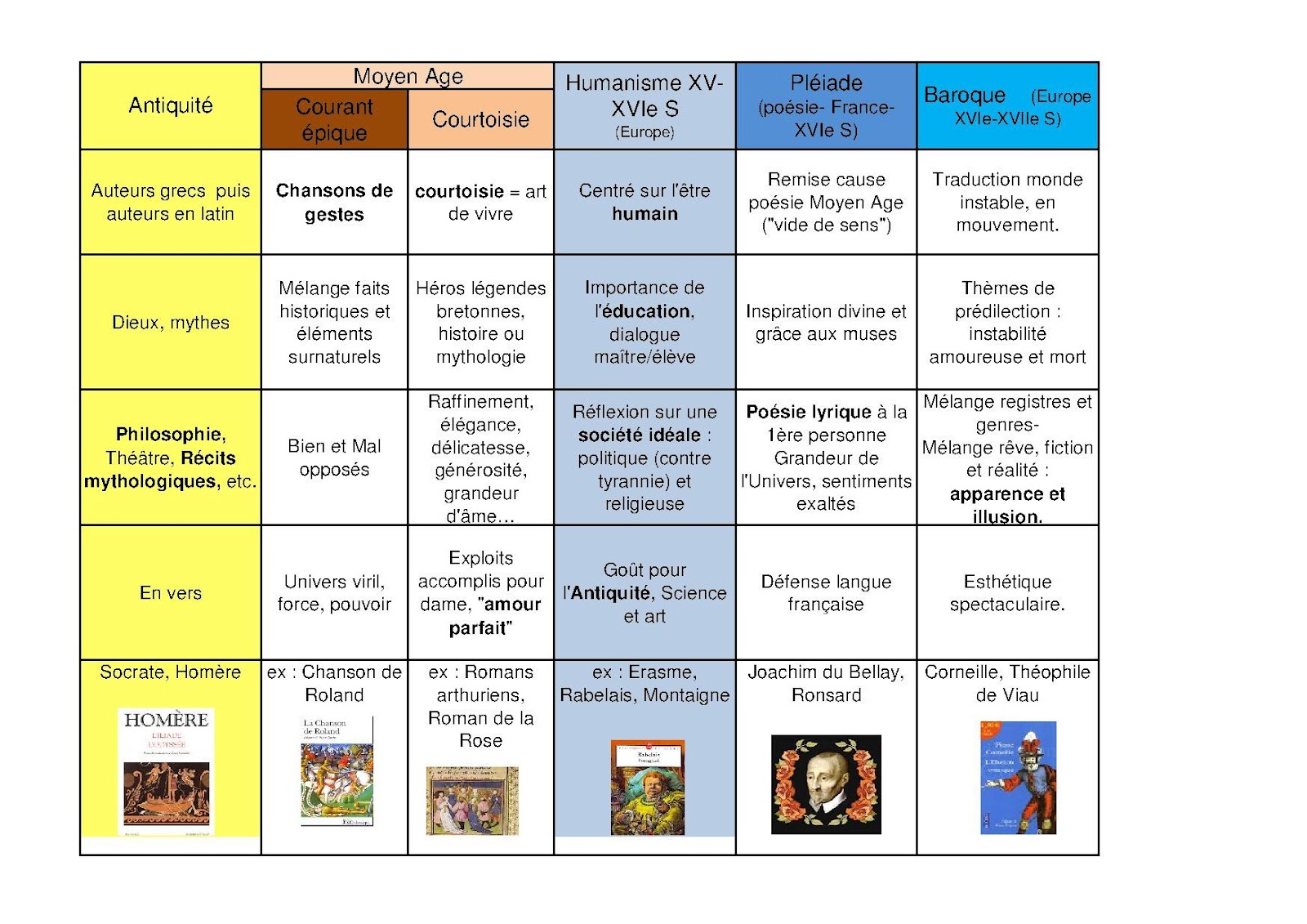
Frise Chronologique Auteurs Et Mouvements Littéraires Noovo Moi

Les mouvements littéraires à connaître Frise chronologique histoire