What is TC and TD on a Pipette?
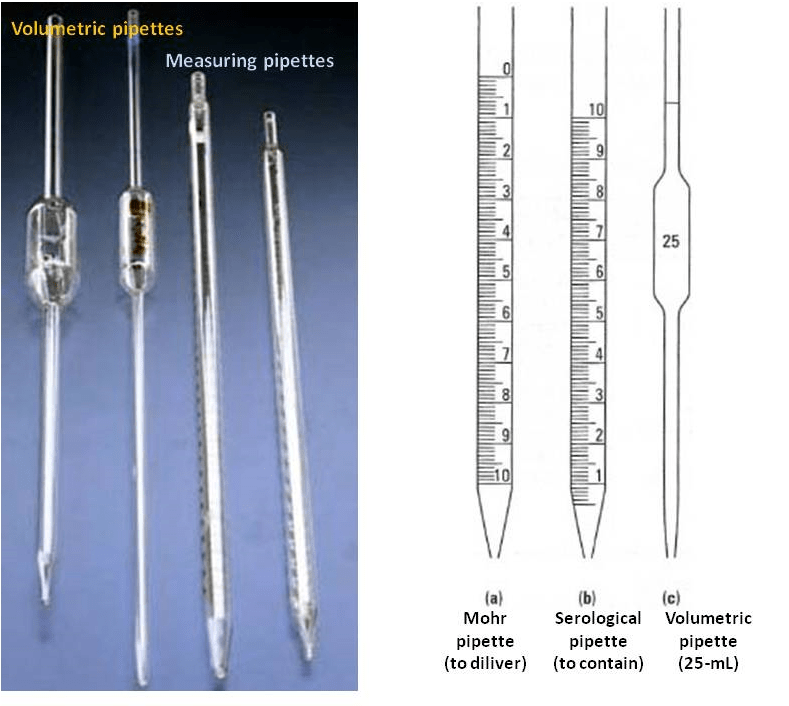
TC and TD on a pipette refer to the volume of liquid that the pipette can dispense. TC stands for "to contain," and TD stands for "to deliver." The TC volume is the maximum volume of liquid that the pipette can hold without overflowing. The TD volume is the volume of liquid that the pipette will dispense when it is fully depressed.
It is important to use the correct TC and TD volumes for your experiment. If you use a TC volume that is too small, the pipette may overflow. If you use a TD volume that is too large, the pipette may not dispense the correct amount of liquid.
Pipettes are commonly used in laboratories to measure and dispense small volumes of liquid. They are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, and can be used to dispense volumes ranging from a few microliters to several milliliters.
What is TC and TD on a Pipette?
TC and TD on a pipette are important specifications that indicate the capacity and accuracy of the pipette. TC stands for "to contain," while TD stands for "to deliver." Here are 5 key aspects to consider:
- Volume: TC and TD volumes specify the range of liquid volumes that the pipette can handle.
- Accuracy: TD volume ensures the precise delivery of the intended liquid volume.
- Calibration: TC and TD volumes are factory-calibrated to meet specific accuracy standards.
- Precision: Pipettes with smaller TC and TD volumes offer higher precision in dispensing small volumes.
- Applications: TC and TD volumes determine the suitability of pipettes for various laboratory tasks.
In summary, TC and TD on a pipette are crucial for accurate and precise liquid handling. By understanding these specifications, researchers can select the appropriate pipette for their specific application.
Volume
The TC and TD volumes of a pipette are directly connected to the pipette's ability to handle specific volumes of liquid. The TC (to contain) volume represents the maximum volume of liquid that the pipette can hold without overflowing. The TD (to deliver) volume, on the other hand, represents the volume of liquid that the pipette will dispense when fully depressed.
Understanding the TC and TD volumes of a pipette is crucial for accurate and precise liquid handling. When selecting a pipette for a specific application, researchers must consider the volume range required for their experiment. Using a pipette with an inappropriate TC or TD volume can lead to errors in liquid measurement and dispensing.
For instance, if a researcher needs to dispense a volume of 100 microliters, they would need to select a pipette with a TD volume of 100 microliters or higher. Using a pipette with a TD volume lower than 100 microliters would result in an inaccurate delivery of the desired volume.
In summary, the TC and TD volumes of a pipette are essential considerations for accurate liquid handling. By understanding the connection between these volumes and the pipette's functionality, researchers can select the appropriate pipette for their specific experimental needs.
Accuracy
The TD (to deliver) volume of a pipette plays a critical role in ensuring the precise delivery of the intended liquid volume. Here are key details to consider:
- Calibration: TD volume is factory-calibrated to meet specific accuracy standards. This calibration ensures that the pipette consistently dispenses the intended volume within a specified margin of error.
- Precision: Pipettes with smaller TD volumes offer higher precision in dispensing small volumes. This is particularly important in applications where precise delivery of small liquid volumes is crucial, such as in molecular biology or analytical chemistry.
- Consistency: The TD volume ensures consistent delivery of the intended volume across multiple dispenses. This consistency is essential for experiments that require precise and reproducible results.
- Accuracy Verification: Researchers can verify the accuracy of their pipettes by performing regular calibration checks. This involves dispensing a known volume of liquid and comparing it to the expected value.
In summary, the TD volume of a pipette is a critical factor that contributes to the accurate and precise delivery of liquid volumes. Understanding the importance of TD volume enables researchers to select the appropriate pipette for their specific experimental needs.
Calibration
The calibration of TC and TD volumes on pipettes is a crucial aspect of ensuring accurate and precise liquid handling. Here are several key points to consider:
- Traceability to Standards: During calibration, TC and TD volumes are traceable to national or international standards, ensuring their accuracy and reliability.
- Quality Control: Calibration serves as a quality control measure, verifying that the pipette meets the manufacturer's specifications and performs within acceptable tolerances.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular calibration is essential to maintain the accuracy and precision of pipettes over time, especially after heavy usage or accidental drops.
By understanding the importance of calibration for TC and TD volumes, researchers can ensure that their pipettes are delivering the intended volumes with the required accuracy and precision. Proper calibration contributes to the overall quality and reliability of experimental results.
Precision
The precision of a pipette refers to its ability to consistently dispense the same volume of liquid multiple times. Pipettes with smaller TC and TD volumes offer higher precision, particularly when dispensing small volumes of liquid.
- Accuracy vs. Precision: Accuracy refers to the closeness of the dispensed volume to the intended volume, while precision refers to the consistency of the dispensed volume across multiple dispenses. Pipettes with smaller TC and TD volumes excel in precision, ensuring that small volumes of liquid are dispensed with minimal variation.
- Reduced Evaporation: Smaller TC volumes minimize the surface area of the liquid exposed to air, reducing evaporation and ensuring more accurate dispensing of small volumes.
- Enhanced Control: Pipettes with smaller TD volumes provide finer control over the dispensed volume, allowing researchers to precisely deliver small volumes of liquid without over-dispensing.
Understanding the connection between precision and TC/TD volumes is crucial for selecting the appropriate pipette for specific experimental needs. Pipettes with smaller TC and TD volumes are particularly valuable in applications where precise and reproducible dispensing of small liquid volumes is essential, such as in molecular biology, analytical chemistry, and drug discovery.
Applications
The volumes of TC (to contain) and TD (to deliver) on a pipette play a crucial role in determining its suitability for specific laboratory tasks. Understanding the relationship between TC/TD volumes and pipette applications is essential for selecting the most appropriate pipette for each experimental need.
- Microliter-Range Pipetting: Pipettes with small TC and TD volumes, typically in the microliter range, are ideal for dispensing precise volumes of small liquid samples. These pipettes are commonly used in molecular biology, biochemistry, and analytical chemistry, where accurate and reproducible dispensing of small volumes is crucial.
- Milliliter-Range Pipetting: Pipettes with larger TC and TD volumes, typically in the milliliter range, are suitable for dispensing larger volumes of liquid. These pipettes are often used in cell culture, microbiology, and general laboratory applications where larger volumes of reagents or samples need to be handled.
- Specialized Applications: Some pipettes are designed with specific TC and TD volumes to meet the requirements of specialized applications. For instance, pipettes with extended TC volumes are available for applications where larger volumes of liquid need to be aspirated but only a portion needs to be dispensed. Conversely, pipettes with reduced TD volumes are available for applications where precise dispensing of extremely small volumes is required.
- Multi-Channel Pipetting: Multi-channel pipettes have multiple channels, each with its own TC and TD volume. These pipettes are designed for simultaneous dispensing of identical volumes into multiple wells or tubes, increasing efficiency and reducing the risk of errors in repetitive pipetting tasks.
By considering the TC and TD volumes in relation to the specific laboratory task, researchers can select the most suitable pipette for their experimental needs, ensuring accurate and precise liquid handling for reliable and reproducible results.
FAQs on "What is TC and TD on a Pipette?"
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions regarding TC (to contain) and TD (to deliver) volumes on pipettes, addressing common concerns and misconceptions.
Question 1: What is the difference between TC and TD volumes on a pipette?
Answer: TC volume refers to the maximum volume of liquid that a pipette can hold without overflowing, while TD volume represents the volume of liquid that is dispensed when the pipette is fully depressed.
Question 2: Why are TC and TD volumes important?
Answer: TC and TD volumes ensure accurate and precise liquid handling. Using the correct volumes prevents overflow, ensures correct dispensing, and contributes to reproducible experimental results.
Question 3: How are TC and TD volumes calibrated?
Answer: TC and TD volumes are factory-calibrated to meet specific accuracy standards, ensuring reliability and traceability to national or international standards.
Question 4: How often should pipettes be calibrated?
Answer: Regular calibration is crucial to maintain accuracy and precision. The frequency of calibration depends on factors such as usage frequency, accidental drops, and manufacturer's recommendations.
Question 5: What is the significance of precision in TC and TD volumes?
Answer: Precision refers to the consistency of dispensed volumes. Pipettes with smaller TC and TD volumes offer higher precision, enabling precise and reproducible dispensing of small liquid volumes.
Question 6: How do TC and TD volumes impact pipette selection?
Answer: Understanding TC and TD volumes is crucial for selecting the appropriate pipette for specific experimental needs, ensuring accurate and precise liquid handling.
By addressing these common questions, this FAQ section provides a comprehensive understanding of TC and TD volumes on pipettes, their significance, and their implications for accurate and reliable liquid handling in laboratory applications.
Transition to the next article section:
For further in-depth exploration of TC and TD volumes, please refer to the detailed sections below.
Conclusion
TC (to contain) and TD (to deliver) volumes are fundamental specifications that define the capacity and accuracy of pipettes. Understanding these volumes is crucial for selecting the appropriate pipette for specific experimental needs and ensuring accurate and precise liquid handling.
Throughout this exploration, we have examined the importance of TC and TD volumes in pipette calibration, precision, and suitability for various applications. By considering the relationship between these volumes and the specific laboratory task, researchers can make informed decisions in pipette selection, leading to reliable and reproducible experimental results.
Unraveling Date Hierarchy Conundrums: A Comprehensive Guide To Eliminating It In Power BI
Landlords And Car Ownership: Can They Ask?
Soaring Temperatures: Has The Mercury Ever Hit 50 Degrees?

The Importance Of The Transition Dipole Moment In Chemistry
Difference Between Tc And Td Pipettes titanmax

Types Of Pipets My XXX Hot Girl