How to Calculate IRR: A Comprehensive Guide
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a crucial financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. It represents the annualized rate of return that an investment is expected to generate over its lifetime, taking into account the time value of money. Calculating IRR accurately is essential for making informed investment decisions.
There are several methods to calculate IRR, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. One common method is the iterative approach, which involves using a financial calculator or spreadsheet to guess and check different discount rates until the net present value (NPV) of the investment is zero. Another method is the graphical approach, which plots the NPV of the investment at different discount rates and finds the point where the NPV crosses the x-axis.
IRR is a valuable tool for investors because it provides a standardized way to compare different investment opportunities. It can help investors identify investments with the highest potential return and make informed decisions about which investments to pursue. However, it's important to note that IRR has limitations and should be used in conjunction with other financial metrics to make investment decisions.
To learn more about IRR and how to calculate it, continue reading this comprehensive guide. We'll cover the different methods for calculating IRR, discuss its importance and benefits, and provide examples to help you understand how to use IRR in your own investment analysis.
How to Calculate IRR
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a crucial financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. It represents the annualized rate of return that an investment is expected to generate over its lifetime, taking into account the time value of money. Calculating IRR accurately is essential for making informed investment decisions.
- Definition: IRR is the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of an investment equal to zero.
- Importance: IRR is a valuable tool for investors because it provides a standardized way to compare different investment opportunities and identify those with the highest potential return.
- Methods: There are several methods to calculate IRR, including the iterative approach and the graphical approach.
- Limitations: IRR has limitations and should be used in conjunction with other financial metrics to make investment decisions.
- Applications: IRR is used in a wide range of investment applications, including capital budgeting, project evaluation, and portfolio management.
- Example: An investment with an initial cost of $100,000 and expected cash flows of $20,000 per year for five years has an IRR of 10%.
These key aspects provide a comprehensive overview of how to calculate IRR and its importance in investment analysis. By understanding these aspects, investors can make more informed decisions about which investments to pursue.
Definition
The definition of IRR establishes the fundamental relationship between the discount rate and the net present value (NPV) of an investment. It provides the basis for understanding how IRR is calculated and used in investment analysis.
- Facet 1: Role of Discount Rate
The discount rate is a crucial factor in IRR calculations. It represents the rate at which future cash flows are discounted back to their present value. A higher discount rate results in a lower IRR, and vice versa. This facet highlights the significance of selecting an appropriate discount rate, which is often based on the risk and time horizon of the investment.
- Facet 2: NPV and Investment Value
The NPV of an investment is the sum of all future cash flows, discounted back to the present using a specific discount rate. A positive NPV indicates that the investment is expected to generate a return that exceeds the cost of capital, while a negative NPV suggests that the investment is not financially viable. This facet explains how IRR is directly related to the NPV and can be used to determine whether an investment is worthwhile.
- Facet 3: IRR as a Decision-Making Tool
IRR is a valuable tool for investment decision-making. By comparing the IRR of different investment opportunities, investors can identify those with the highest potential return. This facet emphasizes the practical application of IRR in capital budgeting and project evaluation.
In summary, understanding the definition of IRR is essential for calculating and interpreting IRR in the context of investment analysis. The facets discussed above provide a comprehensive view of the role of discount rate, NPV, and IRR in investment decision-making.
Importance
IRR plays a crucial role in investment analysis by offering a standardized approach to evaluate and compare different investment opportunities. By calculating the IRR of each opportunity, investors can gain insights into their potential profitability and make informed decisions about which investments to pursue.
- Facet 1: Consistent Evaluation Framework
IRR provides a consistent framework for evaluating investments, regardless of their size, industry, or risk profile. It allows investors to compare different opportunities on an equal footing, ensuring that their decisions are based on objective and comparable data.
- Facet 2: Focus on Future Cash Flows
IRR considers the time value of money and focuses on the future cash flows generated by an investment. This approach helps investors identify opportunities that may have a lower initial cost but generate higher returns over the long term.
- Facet 3: Internal Rate of Return vs. Other Metrics
IRR is a more comprehensive measure of profitability than other metrics such as payback period or accounting rate of return. It takes into account the entire cash flow pattern of an investment, providing a more accurate assessment of its potential return.
- Facet 4: IRR and Investment Decisions
By comparing the IRRs of different investment opportunities, investors can identify those with the highest potential return and make informed decisions about where to allocate their capital. This helps them optimize their investment portfolio and maximize their overall returns.
In summary, the importance of IRR as a standardized tool for comparing investment opportunities stems from its ability to provide a consistent evaluation framework, focus on future cash flows, offer a comprehensive measure of profitability, and guide investment decisions.
Methods
Calculating IRR accurately is crucial for making informed investment decisions. There are several methods available to calculate IRR, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of method depends on factors such as the complexity of the investment and the available data.
- Facet 1: Iterative Approach
The iterative approach involves using a financial calculator or spreadsheet to guess and check different discount rates until the net present value (NPV) of the investment is zero. This method is relatively straightforward and easy to implement, but it can be time-consuming for complex investments with multiple cash flows.
- Facet 2: Graphical Approach
The graphical approach involves plotting the NPV of the investment at different discount rates and finding the point where the NPV crosses the x-axis. This method provides a visual representation of the relationship between the discount rate and the NPV, making it easier to identify the IRR.
- Facet 3: Other Methods
In addition to the iterative and graphical approaches, there are other methods for calculating IRR, such as the modified internal rate of return (MIRR) and the weighted average cost of capital (WACC). These methods are more complex and may be more appropriate for certain types of investments.
Understanding the different methods for calculating IRR is essential for investors who want to make informed investment decisions. By choosing the appropriate method and applying it correctly, investors can accurately determine the IRR of an investment and assess its potential profitability.
Limitations
Understanding the limitations of IRR is crucial when calculating and interpreting its value in investment analysis. IRR, while a valuable tool, has certain constraints that investors should be aware of to make well-informed investment decisions.
- Facet 1: Single Rate Assumption
IRR assumes a single discount rate for all cash flows throughout the investment period. However, in reality, interest rates and investment returns can fluctuate over time. This limitation can lead to inaccuracies in IRR calculations, especially for long-term investments.
- Facet 2: Ignores Risk and Uncertainty
IRR does not explicitly consider risk and uncertainty in its calculations. It treats all cash flows as equally certain, which may not be realistic. This limitation can lead to overestimating the potential return of risky investments.
- Facet 3: Multiple IRRs
In some cases, an investment can have multiple IRRs, which can be confusing and misleading. This limitation arises when the cash flow pattern of the investment is complex and non-conventional.
- Facet 4: Complements to IRR
To overcome the limitations of IRR, investors should use it in conjunction with other financial metrics such as payback period, net present value (NPV), and return on investment (ROI). These metrics provide different perspectives on the investment's profitability and risk, helping investors make more informed decisions.
By considering the limitations of IRR and supplementing it with other financial metrics, investors can gain a more comprehensive understanding of an investment's potential return and make wiser investment choices.
Applications
The calculation of IRR is intricately tied to its diverse investment applications, providing valuable insights for decision-making. Understanding these applications enhances the significance of IRR in the field of finance.
- Facet 1: Capital Budgeting
IRR plays a pivotal role in capital budgeting, which involves evaluating long-term investment projects. By calculating the IRR of each project, businesses can compare and select the ones with the highest potential return on investment. This helps optimize capital allocation and maximize overall profitability.
- Facet 2: Project Evaluation
IRR is a crucial metric in project evaluation, enabling businesses to assess the viability and profitability of individual projects. It provides a comprehensive measure of a project's return, considering the time value of money and the cash flows generated over its lifespan.
- Facet 3: Portfolio Management
IRR is used in portfolio management to evaluate the performance of investment portfolios. By calculating the IRR of each asset or the portfolio as a whole, investors can assess the overall return and compare it to benchmarks or other investment opportunities.
In summary, the applications of IRR in capital budgeting, project evaluation, and portfolio management underscore its versatility as a financial metric. Calculating IRR empowers investors and businesses with a standardized and comprehensive approach to decision-making, enabling them to optimize their investments and achieve their financial goals.
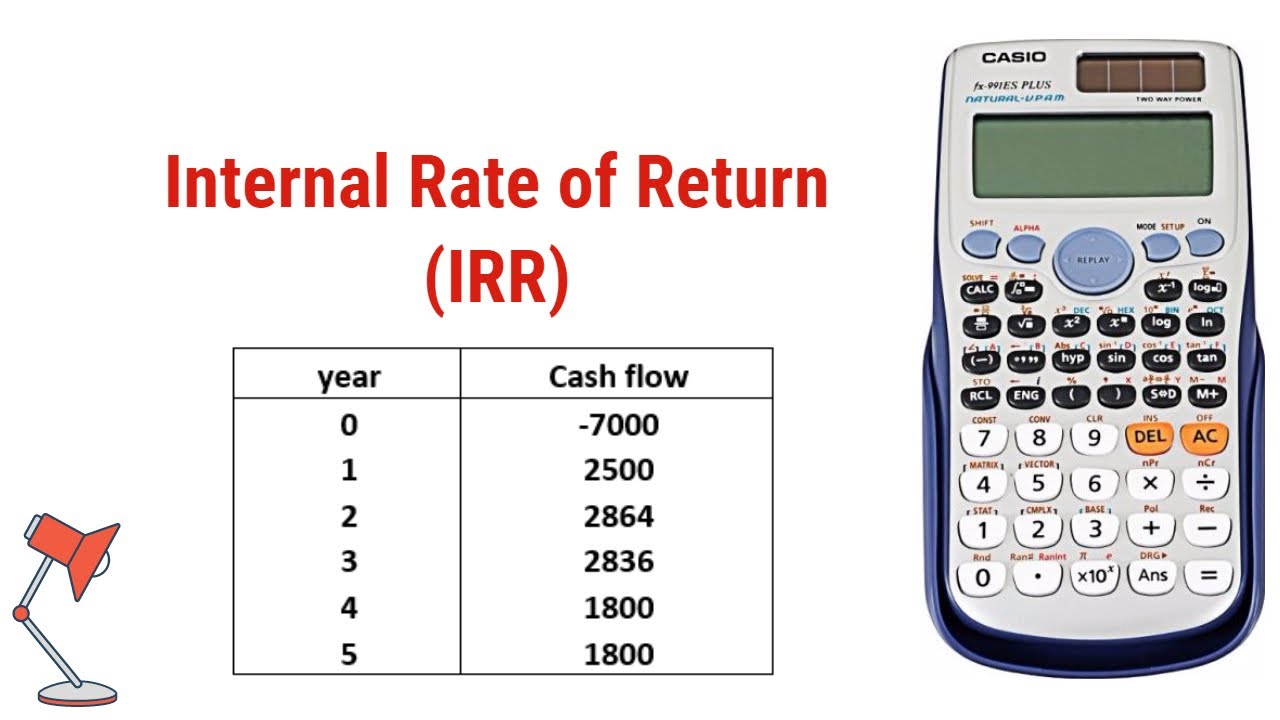
Example
This example illustrates the concept of IRR and demonstrates how it is calculated. The IRR is the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of an investment equal to zero. In this example, the NPV is calculated as follows:
NPV = -100,000 + 20,000/(1+0.10)^1 + 20,000/(1+0.10)^2 + 20,000/(1+0.10)^3 + 20,000/(1+0.10)^4 + 20,000/(1+0.10)^5
NPV = $0
Since the NPV is zero, the IRR is 10%. This means that the investment is expected to generate a return of 10% per year over its five-year life.
This example is a simplified illustration of how to calculate IRR. In practice, IRRs are often calculated using financial calculators or spreadsheet software. However, the underlying concept is the same: the IRR is the discount rate that makes the NPV of an investment equal to zero.
Understanding how to calculate IRR is important for investors because it allows them to compare different investment opportunities and make informed decisions about which investments to pursue. IRR is a valuable tool for evaluating the profitability of an investment and can help investors maximize their returns.
FAQs about How to Calculate IRR
Calculating the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a crucial aspect of investment analysis. Here are some frequently asked questions to enhance your understanding of IRR calculations:
Question 1:What is the significance of IRR in investment decision-making?
Answer: IRR plays a vital role in investment decision-making by providing a standardized metric for comparing different investment opportunities. It enables investors to identify investments with the highest potential return, considering the time value of money and the cash flows generated over the investment period.
Question 2:What are the key steps involved in calculating IRR?
Answer: Calculating IRR involves determining the discount rate that equates the net present value (NPV) of an investment to zero. This can be done using iterative or graphical approaches.
Question 3:When is the iterative approach used for IRR calculation?
Answer: The iterative approach is commonly used when the cash flows of an investment are complex or non-uniform. It involves using a financial calculator or spreadsheet to guess and check different discount rates until the NPV becomes zero.
Question 4:What is the graphical approach to IRR calculation?
Answer: The graphical approach involves plotting the NPV of an investment at different discount rates. The IRR is the discount rate where the NPV line intersects the x-axis.
Question 5:Are there any limitations to using IRR?
Answer: Yes, IRR has certain limitations. It assumes a single discount rate for all cash flows, does not explicitly consider risk, and can sometimes result in multiple IRR values for complex cash flow patterns.
Question 6:How can investors use IRR effectively?
Answer: Investors can leverage IRR to compare investment opportunities, evaluate the profitability of projects, and make informed decisions about capital allocation. It should be used in conjunction with other financial metrics to gain a comprehensive understanding of an investment's risk and return profile.
Understanding these FAQs provides a solid foundation for calculating and interpreting IRR in investment analysis. By considering the nuances and limitations of IRR, investors can make more informed investment decisions and achieve their financial goals.
Transition to the Next Article Section:
To further enhance your knowledge about IRR, explore the following section, where we delve into advanced concepts and applications of IRR in investment analysis.
Conclusion
The exploration of "how to calculate IRR" has provided a comprehensive understanding of this critical financial metric used in investment analysis. IRR empowers investors with a standardized tool to evaluate and compare investment opportunities, enabling them to make informed decisions about capital allocation. By calculating IRR accurately and considering its limitations, investors can optimize their investment portfolios and maximize their returns.
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the significance of IRR remains steadfast. Understanding how to calculate IRR equips investors with the knowledge to navigate complex investment scenarios and make well-informed choices. By incorporating IRR into their investment analysis toolkit, investors can gain a competitive edge and achieve their long-term financial goals.
The Ultimate Guide To Optometry: Measuring Vision Accuracy With Precision
How Much Is That Vintage Sewing Machine Worth?
Ultimate Guide To Phototropism Examples: Uncovering Plant's Remarkable Light-Seeking Behavior
How To Calculate Irr Calculator Haiper

Internal Rate of Return Formula How to Calculate IRR

What is IRR? Formula, Calculation, Examples Bizness Professionals